Drivers of Modern Distributed Systems
- Pervasive(spread throughout蔓延的) networking technology
- Ubiquitous(existing at the same time 普及的) computing
- multimedia services
- utility computing: providing computing resources as a service, without users to invest in
Pervasive Networking
- ability to access and connect to networks anytime and anywhere, using a variety of devices and technologies
Ubiquitous Computing
- embedding computing devices and technologies into everyday objects and environments
- making them unobtrusive(不引人注目的), invisible and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives
- supports user mobility, allows user to remain connected to an environment as the user moves about
- possible because of the high portability of many of these devices
Multimedia Services多媒体
- a range of media types in an integrated manner
Utility Computing效用计算
在这个模型里服务提供商提供客户需要的计算资源和基础设施管理,并根据应用所占用的资源情况进行计费,而不是仅仅按照速率进行收费
Utility Computing —> Clout Computing
- cloud is defined as a set of internet-based application, storage and computing services to support users’ needs
Cloud Computing
- promotes everything as a service, reducing requirements on users’ devices
- Internet of Things(IoT) and Big Data are closely related to cloud computing
- networked society
- implemented on cluster computer
- overall goal is to provide a range of cloud services, including high performance computing capability
Grid Computing
grid focus on high-end data-heavy or computationally expensive applications
cloud is more general
grid is and early example of cloud computing, but cloud computing has developed significantly since then
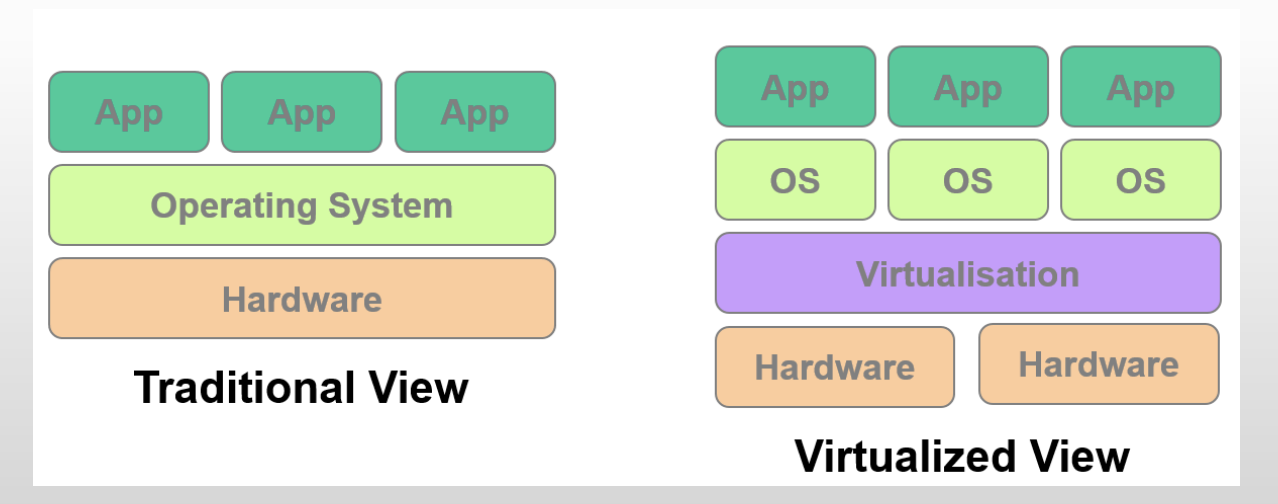
Key Concept: Virtualisation